What is Ethereum? What to Expect From Ethereum 2.0?

- By Pierre-Alexandre
July 25th, 2019
Here’s everything you need to know about the Ethereum network and the major upgrades it plans to introduce with Ethereum 2.0.
Introduction
As such, Ethereum needs no introduction! While Bitcoin is known for popularizing the blockchain technology, Ethereum is well-known for popularizing concepts like decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts in the blockchain industry.
As defined by Wikipedia, “Ethereum is an open-source, public, blockchain-based distributed computing platform and operating system”. Ether (ETH) is the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum platform and currently ranks second as the most-valued cryptocurrency by market cap, after Bitcoin.
The Ethereum ecosystem and developers are currently working on a major platform overhaul called Ethereum 2.0, scheduled to go live in early January 2020. This overhaul comes to meet the demand of blockchain advancements Like scalability, speed, better consensus mechanism, and other improvements.
Some of the important updates for Ethereum 2.0 include Plasma, Raiden Sharding, Proof-of-Stake, eWASM, Serenity, zk-snarks, etc. While we will be discussing all these ahead in the article let’s go through the basic understanding Ethereum.
The History of Ethereum Updates/ Ethereum Lineage
Cryptocurrency programmer and researcher Vitalik Buterin proposed the idea of Ethereum in late 2013. At an early age of 17, Buterin was intrigued by the concept of blockchain technology and got involved himself in Bitcoin programming during 2011. At the same time, he also went to co-found the most popular crypto and blockchain publication Bitcoin Magazine.
During his working as a Bitcoin-programmer, Buterin envisioned a blockchain-based decentralized platform beyond just the financial use-case presented by Bitcoin. Buterin said:
“I thought [those in the Bitcoin community] weren’t approaching the problem in the right way. I thought they were going after individual applications; they were trying to kind of explicitly support each [use case] in a sort of Swiss Army knife protocol.”
In 2014, Buterin and his team of other co-founders launched the Ethereum blockchain network through a crowdfunding campaign. The team managed to raise a whopping $18 million and by 2015, they launched the first live release of Ethereum called the Frontier.
Global developers and business started to recognize the potential of the Ethereum platform and soon they joined the Ethereum ecosystem by working on different use cases.
As on date, Ethereum’s infrastructure that hosts decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts is widely leveraged by developers and businesses. Besides, popular decentralized games like CryptoKitties has taken the platform by storm.
During the crypto mania of late 2017, the ETH price hit its all-time high of $1400 and it was the same period when the Ethereum platform faced some major roadblocks. The existence of several stakeholders cluttered the network which then faced issues about network speed and scalability.
In 2016, nearly $50 million worth ETH tokens were stolen that raised several questions on the network security. Later in the investigation, it was discovered that the theft happened due to the exploitation of a flaw in the smart contract software of the DAO project.
Following this incident, there were cracks in the Ethereum community that resulted in the splitting of the Ethereum platform into two different blockchains: Ethereum (ETH) and Ethereum Classic (ETC).
In March 2017, some Fortune 500 companies, blockchain startups, and other research groups announced joining the Enterprise Ethereum Alliance (EEA). The EEA is a non-profit organization and focuses on the development of blockchain-based enterprise solutions.
It has some big names like the CME Group, ConsenSys, Deloitte, JP Morgan, Microsoft, Intel, Cornell University's research group, Samsung SDS, Toyota Research Institutes, and other as its existing members.
Ethereum features.
Let us take a look at some of the most popular features of the Ethereum blockchain network: Smart Contracts, Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), Decentralized Applications (DApps), and DAO.
- Smart Contracts
What Are Smart Contracts?
The smart contracts concept was first visualized long back in 1994 by cryptographer and legal scholar Nick Szabo. He came to realize that some self-executable contracts can be deployed on a distributed ledger, which were later termed as smart contracts.
Thus a smart contract is basically a computer code or protocol that can digitally verify and facilitate the execution of a contract without the involvement of a third party. They are supervised by a network of computers running the blockchain network, in this case, the Ethereum.
The smart contracts can be used to execute the different process as well as transactions once the pre-required conditions are met. Thus, smart contracts are one of the most-effective ways to exchange value in an absolute conflict-free manner.
Note that the job of the smart contracts is to only execute the rules and not define them. Thus, the two people engaging in a smart contract can priorly formulate the rules of their contracts.
How Do Smart Contracts Work?
Smart Contracts find their application in several fields like insurance, healthcare, and financial services. Moreover, as the world gets deeply interconnected through the internet, smart contracts help to bring workflow transparency to the internet.
To understand the workings of the smart contracts, let us take the example of a freelancing gig economy. Currently, freelancers connect with their clients through a third-party interface or platforms.
These platforms often act as escrow agents which control the flow of funds between the freelancer and the job provider. Thus, both the parties have to trust such third-party platforms for exchanging their funds.
Smart contracts help to eliminate such intermediaries. Consider that a project needs to be executed into five different stages. So, before creating a smart contract, the freelancer and the client can discuss the amount of work needed to be done in each stage. Both of them can mutually discuss the conditions needed to be met for completion of each stage, and the payments associated with it.
Now, when the freelancer submits the work, the smart contract will check if the conditions are met and will automatically release the funds or the payments. This helps to have better transparency in the workflow thereby creating an atmosphere of trust.
Some of the key benefits of blockchain-based smart contracts are that they are "trustless", cost-effective, accurate, autonomous, and fast in execution. - Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)
What is Ethereum Virtual Machine?
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) looks after the execution of contract bytecode. They are visually stacked into each Ethereum full node. Note that most of the sort contracts on the blockchain are written in high-level languages like Solidity, Javascript, C++, and others.
However, the languages cannot be directly executed by the EVM. Hence, the smart contracts are basically compiled into low-language machine instructions called the opcodes. Thus, the machine code remains completely isolated from the file system, the network, and other processes of the host computer.
How Does Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) Work?
Each node on the Ethereum blockchain network first runs on the EVM instance. This allows the node to arrive at a mutual consensus and execute the same instructions. The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is the most vital ingredient to the consensus engine of the Ethereum platform. It helps to execute the smart contracts in a trustless and deterministic manner.
The EVM is often referred to as Turing Complete which refers to a system that can perform any logical step of a computational functional. Thus, the Ethereum platform acts as a peer-to-peer worldwide computer, working somewhat similar to the internet.
As earlier stated, the Ethereum platform has several use-cases for transfer of value, unlike the Bitcoin network which can only be used for financial transactions. The EVM achieves Turing completeness by creating an economic ecosystem which charges on every software instruction execution instead of for each financial transaction.
For a deeper understanding of the working of EVM opcodes and bytecodes, please refer to this article. - Decentralized Applications (DApps): Today, a number of blockchain projects and platform host decentralized application (DApps), however it was Ethereum who first presented the magic of DApps.
Some of the essential features of DApps are that they are completely open-source allowing anyone to seen and contribute to its code. As per the name, DApps are completely decentralized and implemented on a blockchain platform. Besides, they have a built-in consensus mechanism and are fuelled by cryptocurrency tokens or digital assets.
The Ethereum whitepaper splits DApps into three different categories: DApps that manage money, DApps that manage money with other project execution part, and DApps falling in the “other” category.
In the first type, two individuals can settle contracts using ETH tokens as a way of exchange. The DApps uses Ethereum’s network nodes to facilitate data distribution.
The other types of DApps are the ones that involve money using outside information. Consider the case of claiming a medical policy. Suppose that a policy implements DApp to automatically pay out the diseased as they upload their medical bills. DApps help to make the entire process completely transparent and faster.
The “other” types of DApps can be used by government organizations or businesses, e.g. creating a transparent and tamper-proof voting system. - Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO): As the name suggests, DAO aims to automate certain processes in an organization without any intervention of the hierarchal management.
The DAO process could involve anything like the digital implementation of salary structures and rise once the company reaches certain annual revenues or profits.
However, the DAO concept has still not resonated much the existing organizations as there are some things yet to be solved.
Back in 2016, a project called “The DAO” was first launched. It allowed participants to purchase the DAO tokens and vote for the projects they would like to fund. The project relied on the “wisdom of crowds” concept for selecting the projects.
However, the project failed within a few months as DAOs functions relied completely on smart contracts and pre-programmed rules. The reason behind the project closure is that although the smart contract looks lucrative from the value proposition, it’s difficult to change them once deployed on the blockchain.
Now, this immutability of smart contracts might seem a good feature but just in case there are any sudden changes in the organizational level, the DAO won’t allow to implement them once created. Moreover, if a DAO has any bug, it can be rectified at a later stage. Hence, due to this major shortcoming, organizations have refrained from using this model.
Ethereum And its Business Use Cases
The power of the Ethereum network has been acknowledged not only by blockchain enthusiasts but by several global organizations. As stated earlier, these organizations together have formed the Ethereum Enterprise Alliance (EEA), a consortium of blockchain startups, banks, governments, non-profits, and other global organizations.
The enterprise Ethereum is an effort to allow companies to have private and hybrid implementations of the Ethereum codebase for different business applications. The platform allow companies to build, test and deploy DApps while leveraging some blockchain benefits like fraud prevention, immutability, no downtime, or prevention of third-party interference.
As explained by ConsenSys, some of the key benefits of Enterprise Ethereum are:
- Improve operational efficiency and business network accountability
- Reduce costs of coordination and trust with external parties
- Discover new business models around digital assets through multi-sided markets
- Make business future-proof against outdated process models.
The members of the EEA can create business DApps across different fields like International Trade and Commodities, Supply Chain, Banking & Finance, Energy, Identity Authentication, Real Estate, Healthcare, Government, Media and Entertainment, and many more.
More than 200 members have currently pledged their membership to the Ethereum Enterprise Alliance (EEA). Some of the big corporations developing their blockchain solutions on Ethereum include Amazon, Citigroup, Fidelity, Metlife, Google, Microsoft, Coinbase, Google, Samsung, etc.
As said, Ethereum has some potential competitors in the market now like Tron, EOS, Stellar, NEO, and others. Earlier this year in April 2019, Tron founder Justin Sun spoke about a potential collaboration with Ethereum. During a podcast interview with The Crypto Chick Sun spoke about the official collaboration.
Sun said: “I think in the future we will even collaborate with lots of Ethereum developers and also the enterprises built on Ethereum before to make the industry better.”
Ethereum Problems and Issues
Ethereum has had a bumpy ride over the last year as the developers have struggled to overcome the existing challenges with scalability, security and the network consensus model.
With popular DApps like CryptoKitties creating a huge rage, the Ethereum network hit a major bumper with users finding it difficult to perform regular ETH transactions. If the entire Ethereum ecosystem: ETH transactions + Smart Contracts + DApps have to co-exist, scalability and network expansion are one of the utmost priorities.
Ethereum developers have also been struggling to solve the issue with the difficulty bomb. The Difficulty bomb is the complexity of mining new blocks to the ETH network used to rewards the ETH miners. But as the difficulty bomb expands it will take substantially more time to add new blocks to the Ethereum platform.
To solve this, Ethereum is planning to shift from Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake consensus model. This will exponentially reduce the mining incentives and thus the miner dominance.
The Ethereum developers have a huge challenge up their sleeves but they are committed enough to take all matters at hand during the upcoming launch of Ethereum 2.0. But despite these issues, Ethereum’s DApps and smart contracts continue to attract enterprises to its platform.
Andrew Keys, founder of ConsenSys Capital, expects some ground-breaking DApps development ahead in the coming years. Earlier this year, Andrew said:
“Decentralized Finance is already working on public-permissionless Ethereum, and we’ll see a 10x increase in users. While so much development in the Ethereum ecosystem in 2018 has been focused on elements under the hood, it’s through user experience that audiences truly connect with dapps. With a few notable exceptions, design in blockchain has lagged behind the lofty aspirations of its protocol. No longer.”
Ethereum and its main competitors
Over the last few years, several blockchain projects have become popular which address some of the major pain-points of Ethereum like the scalability and network speed. Some of the main competitors to Ethereum are EOS, Cardano, Ethereum Classic, NEO, etc.
- EOS: Over the last few years, EOS has climbed the ladder to emerge as one of the most powerful platforms to create decentralized applications (DApps). The platform is created in such a way that it facilitates easy upgrades and scalability, one of the major issues Ethereum is currently facing. The platform consolidates the DApp and smart contracts feature of Ethereum and the security of the Bitcoin network. It facilitates all tools required by a developer to create full-fledged decentralized applications.
The EOS platform has major features like cloud storage and hosting, shared databases, potentially infinite scaling, account recovery, authentication systems and much more.
The EOS network blocks are structured into “cycles” and are sequentially verified. This helps to considerably reduce latency and keep the network performance at an all-time high. - Ethereum Classic (ETC): This is nothing but an offshoot of the Ethereum mainnet which came into existence with the hard fork of the primary Ethereum network. The Ethereum Classic network thus carries all the features and technicalities of the original Ethereum network but at a reduced cost.
Another good feature of Ethereum Classic is that unlike the ETH, ETC supports irreversible transactions. - NEO: Popularly called as the Chinese Ethereum, NEO is a completely decentralized platform with smart contract functionality without any third-party interference.
NEO competes with Ethereum on a number of factors like higher scalability, multi-language support, higher transaction processing throughput. Learning lessons from the Ethereum/Ethereum classic hardfork debacle, NEO is programmed only to have soft forks and no hard forks. - Qtum: Launched in 2016, combines the elements of Bitcoin’s security and Ethereum’s decentralized apps and smart contracts functionality. To implement the smart contract functionality, the Qtum blockchain features an Abstract Accounting Layer (AAL) through a robust x86 Virtual Machine.
This is basically an off-chain scaling solution similar to Bitcoin’s Lightning Network. However, Qtum’s AAL combines the ability to develop and host smart contracts. The Qtum developers appreciate the presence of the network’s second-layer storage as it facilitates their major aim to build stable business applications. - Cardano: This is a unique platform competing with Ethereum and features a dual-layer solution. The Cardamon blockchain network has a separate account layer and control layer which keeps financial transactions different from the smart contracts.
The Cardano network is developed using the Haskell programming language that is best suited for data analytics and blockchain applications. Cardano has a potential blend of privacy protection and public sector usability that makes it one of the most preferred blockchain platforms in the market.
Ethereum 2.0 & the future.
So as we earlier stated the upcoming Ethereum 2.0 aims to bring some of the underlying issues with the scalability, mining, security, and network performance of the existing Ethereum protocol. The major overhaul with Ethereum 2.0 is moving from the current Proof-of-Work consensus model to the Proof-of-Stake.
Some of the most popular updates with Ethereum 2.0 are Sharding, Plasma, Serenity, Raiden, eWASM, and others.
Back in 2015, the Ethereum launch was scheduled in four different stages. The first stage was called the Frontier which was the initial build during launch and released on July 30, 2015. Soon within less than a year, its second platform upgrade called ‘Homestead’ was released on March 14, 2016.
Ethereum’s third upgrade Byzantium was released on October 16, 2017. Most recently this year on February 28, 2019, Ethereum had undergone the Constantinople upgrade. The next and the final stage is Serenity will take us to the Ethereum 2.0.
Ethereum founder Vitalik Buterin usually refers to the Ethereum 2.0 update as Semantics. Buterin referred to Ethereum 2.0 as
“a combination of a bunch of different features that we’ve been researching, talking about and actively building for several years and that are finally coming together into this one coherent whole.”
Here’s a look at some of the most important features for Ethereum 2.0.
- Proof-of-Stake: With Casper and Beacon-like solutions, it will completely change the way we mine the ETH tokens. The Proof-of-Stake (PoS) gives the stakeholder the authority over network security.
Unlike the Proof-of-Work, the PoS model eliminates the need for cutting edge GPUs, huge power grids and stacks on mining rigs. It is assumed that the PoS model will cut the energy resources required to run the Ethereum network by 99%.
The PoS consensus model will require people to stake their coins and the minimum staking amount will be 32 ETH. Below is the video from BlockGeeks which explains Proof-of-Stake in a simple and lucid manner.
However, the transition to Ethereum 2.0 PoS structure will be smooth. The developers will first launch the Beacon Chain with PoS architecture which will run alongside the existing Ethereum network. Besides launching the PoS protocol, the Beacon Chain will also ensure settlement and finality.
- Plasma and Raiden: Just like Bitcoin’s Lightning Network, the Plasma and Raiden is an extra layer atop the Ethereum mainnet. These two provide off-chain scalability to the Ethereum network and handle massive amounts of transactions.
Just like the Bitcoin SEGWIT, the Ethereum Plasma solution aims to significantly boost the network performance thereby allowing multiple smart contracts to run simultaneously. As we stated earlier that some big enterprises have their DApps running on Ethereum. Thus, Plasma aims to offer the required bandwidth for seamless network performance.
Plasma aims to have a sidechain framework that will effectively reduce congestion on the main chain. This framework will be basically a hierarchically arranged blockchain tree with numerous smaller chains called the Plasma chains.
Each smaller Plasma chain will serve as a customizable smart contract which can be designed to work in a particular way but serving different needs. It means that the Plasma chains can work independently as well as co-exist together. Thus, using the Plasma solution, businesses and enterprise several scalable solutions in multiple different ways. - eWASM: This looks after the quick execution of the code while expanding the coding capabilities and options for the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
WASM basically is the short form used for WebAssembly. It is a sort of Virtual Machine (VM) or a binary code compiles your code for the web. The WASM identifies the hardware on which it is running and optimizes the code execution and load times.
The eWASM is the Ethereum-based WebAssembly. It helps to prevent any non-deterministic behaviour and looks after the faster execution of smart contracts in Ethereum. eWASM is the replacement for the existing Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and would drastically improve the transaction throughput. - Sharding: This is a concept of breaking a larger database into more manageable parts. It stops one single app from creating clutter and addresses the issue of transaction speed and scalability.
With Sharding, the basic concept is eliminating the need of a full node to secure the Ethereum network. Rather than each node storing the complete history of transactions occurring on the platform, sharding allows the nodes only to carry some limited specific information, thereby making the whole network faster. Below is the explanatory video on Sharding.
- Serenity: Well, this is the most important and crucial upgrade of the Ethereum network that creates a Proof-of-Stake chain. The PoS chain enwraps all of the above features like Sharding, eWASM, etc. Serenity is like to enhance the scalability of the current Ethereum network by 1000x.
Developers are working to make the Serenity PoS chain completely compatible with the existing Proof-of-Work chain. The Ethereum developers are also planning to use zk-snarks (zero knowledge of proof) as the temporary scalability solution.
The Serenity implementation will take place in four major stages:
- Phase 0: This phase will include the implementation of the Beacon Chain with PoS protocol. The development of Phase 0 is scheduled to be completed by 2019.
- Phase 1: This will include the release of Shard Chain will be interoperable with the Beacon Chain and will aim to provide network scalability. Phase 1 implementation is scheduled for 2020.
- Phase 2: This will include the implementation of eWASM for faster code execution. Timeline is 2020/2021.
- Phase 3: This will be the continued implementation of improvement in Ethereum’s security and decentralization.
To know more about the working and features of Ethereum 2.0, follow this article by RocketPool.
The Ethereum Roadmap to Serenity:
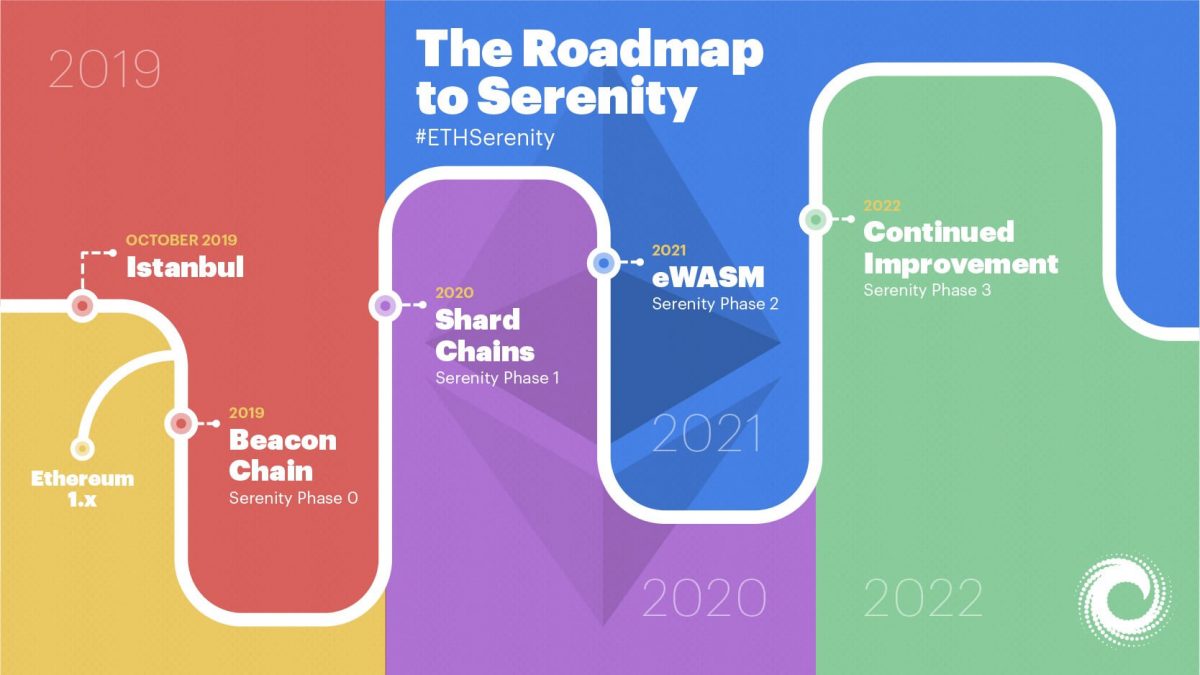
To know more about the working and features of Ethereum 2.0, follow this article by RocketPool.
Conclusion
Despite several other competitors in the market, even today, Ethereum continues to be a top choice for enterprises to create smart contracts and DApps solutions. By solving the issues with scalability and network performance, the Ethereum 2.0 will most likely continue to dominate the blockchain market.